Financial planning is a strategic approach to managing your finances to achieve your life goals. It involves assessing your current financial situation, setting realistic objectives, and creating a roadmap to reach them. By aligning your financial resources with your aspirations, financial planning empowers you to make informed decisions, prioritize spending, and build wealth over time.
Key Takeaways
Financial planning serves as an essential foundation for achieving your financial and life goals by providing a clear, structured roadmap that aligns your resources with your ambitions. It begins with setting specific and realistic goals, followed by creating actionable steps that prioritize your needs and manage your finances effectively. Through disciplined saving, smart investing, risk management, and tax optimization, financial planning ensures you stay on track despite life’s uncertainties. It also fosters informed decision-making and the flexibility to adjust your plans as circumstances change, helping you maintain momentum and confidence. Ultimately, financial planning transforms your goals from distant dreams into achievable milestones, empowering you to build a secure and fulfilling financial future.
Understanding Financial Planning
At its core, financial planning is about making deliberate choices to ensure that your financial resources are utilized effectively to support your personal and family goals. This process encompasses various aspects, including budgeting, saving, investing, insurance planning, tax strategies, and retirement preparation. Each component plays a vital role in creating a comprehensive plan that addresses both current needs and future aspirations.
Financial planning is more than just managing your money — it’s about creating a comprehensive roadmap to guide your financial decisions, help you reach your goals, and secure your future. Whether you’re planning to buy a home, start a business, send your children to college, or retire comfortably, financial planning is the foundation that supports all of these ambitions.
Below is a detailed breakdown of what financial planning involves, its key components, benefits, and how you can get started.
What is Financial Planning?
At its core, financial planning is the process of evaluating your current financial status, defining your financial goals, and developing a tailored strategy to reach those goals over time. It’s a proactive and structured approach that takes into account every aspect of your personal finances, including income, spending, savings, investments, insurance, and taxes.
Financial planning isn’t a one-time activity — it’s a dynamic and ongoing process. As your circumstances change — such as a new job, marriage, children, or retirement — your financial plan should evolve accordingly.
Objectives of Financial Planning
The key objectives of financial planning include:
- Determining short-term and long-term financial goals
- Assessing current financial resources and obligations
- Creating a strategy to build, manage, and preserve wealth
- Identifying risks and preparing for financial uncertainties
- Ensuring financial independence and stability
- Achieving life goals through systematic financial management
Key Components of Financial Planning
Let’s explore the major components that make up a robust financial plan:
Goal Setting
Every financial plan begins with setting clear, measurable, and realistic goals. These could range from short-term objectives like saving for a vacation, to long-term goals like retirement or purchasing a house. The more specific your goals, the easier it is to formulate a plan to achieve them.
Cash Flow Management
Managing your cash flow involves tracking your income and expenses to ensure you are living within your means. It includes budgeting, controlling unnecessary expenditures, and maximizing savings. This step creates the foundation for wealth building.
Debt Management
Debt is a part of most people’s financial lives, but excessive or mismanaged debt can derail your goals. Financial planning helps you identify good vs. bad debt, create a repayment strategy, and avoid interest traps. Paying down high-interest debt first is usually the priority.
Emergency Fund Planning
An emergency fund is essential for covering unforeseen expenses such as job loss, medical emergencies, or urgent repairs. A well-planned financial strategy recommends saving at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses in a liquid and accessible account.
Investment Planning
This is the engine that drives wealth accumulation. Investment planning involves choosing the right asset classes based on your risk appetite, financial goals, and time horizon. Diversification, asset allocation, and periodic rebalancing are all strategies covered in financial planning.
Insurance and Risk Management
Life is uncertain, and insurance acts as a safety net to protect you and your loved ones from unexpected financial losses. Health, life, disability, and property insurance are all critical elements of a complete financial plan.
Tax Planning
Smart tax planning reduces your tax liability and increases your net returns. Financial planning incorporates strategies to take advantage of deductions, tax-saving instruments, and long-term capital gains treatment.
Retirement Planning
Planning for retirement ensures you can maintain your lifestyle even when you stop earning actively. It involves estimating your retirement needs, deciding on investment vehicles (such as 401(k), IRAs), and preparing for inflation and healthcare costs.
Estate Planning
Estate planning ensures that your assets are passed on according to your wishes. It may include writing a will, setting up trusts, naming beneficiaries, and planning for estate taxes.
Types of Financial Planning
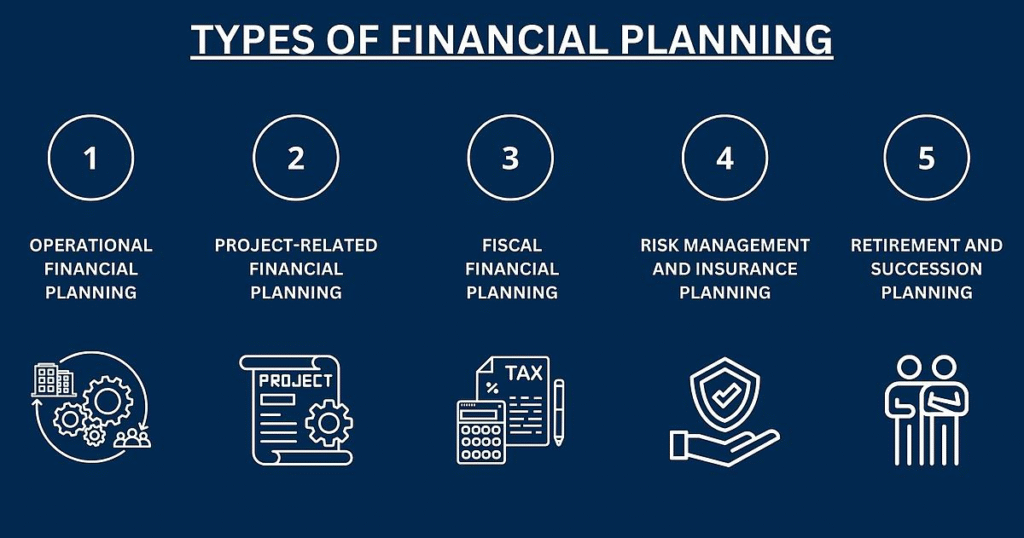
Different goals and life stages require different types of financial planning:
- Personal Financial Planning: Focused on individual needs such as income, budgeting, and saving.
- Family Financial Planning: Involves managing joint finances, planning for children’s education, and retirement.
- Retirement Planning: Specifically targets the financial needs and income streams during retirement years.
- Tax Planning: Helps optimize financial plans to minimize tax burden.
- Investment Planning: Concerned with building an investment strategy to meet financial goals.
- Estate Planning: Centers around asset distribution and legacy creation.
Benefits of Financial Planning
The advantages of financial planning are both tangible and psychological:
- Achieve Financial Goals: Whether it’s buying a car or starting a business, financial planning provides a clear roadmap.
- Improved Financial Literacy: Understanding financial concepts empowers you to make better decisions.
- Security During Emergencies: With a plan in place, you’re better prepared for job losses or medical emergencies.
- Better Standard of Living: Proper budgeting and saving increase your capacity to spend without guilt or stress.
- Reduced Debt Stress: Knowing how to tackle debt efficiently relieves a significant financial burden.
- Wealth Creation and Preservation: Smart investing strategies can multiply your assets while minimizing risk.
- Peace of Mind: Perhaps the most underrated benefit — knowing your financial future is under control.
Who Needs Financial Planning?

Financial planning is not just for the wealthy — it’s for anyone with financial goals. Whether you are a student, a working professional, a parent, or a retiree, financial planning ensures you make the most of your money at every stage in life.
Common Financial Planning Mistakes to Avoid
- Not setting clear goals
- Underestimating expenses
- Ignoring inflation
- Delaying investment
- Failing to plan for emergencies
- Lack of diversification
- Ignoring estate planning
- Overlooking insurance needs
Avoiding these pitfalls can dramatically increase your chances of financial success.
How to Start Your Financial Planning Journey
Assess Your Financial Situation
Calculate your income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and net worth.
Set Specific Goals
Define what you want to achieve financially — short-term, medium-term, and long-term.
Create a Budget
Track your spending and create a budget that supports your goals.
Build an Emergency Fund
Start with a goal of 3–6 months of expenses.
Invest Wisely
Understand your risk tolerance and time horizon, then build a diversified investment portfolio.
Protect with Insurance
Ensure you have adequate life, health, and property coverage.
Plan for Taxes and Retirement
Use tax-efficient strategies and begin saving for retirement early.
Review and Adjust Regularly
Life changes — your plan should, too. Revisit it at least once a year or after major life events.
Tools and Resources for Financial Planning
- Budgeting Apps (e.g., Mint, YNAB, PocketGuard)
- Investment Platforms (e.g., Vanguard, Fidelity, Robinhood)
- Retirement Calculators
- Personal Finance Books
- Financial Advisors and Certified Financial Planners (CFPs)
The Role of Financial Planning in Goal Achievement
| Role of Financial Planning | Description | How It Helps Achieve Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Clear Goal Setting | Defining specific, measurable, and realistic financial goals | Provides direction and focus, making goals tangible and achievable |
| Realistic Roadmap Creation | Developing step-by-step action plans to reach goals | Breaks down large goals into manageable tasks and timelines |
| Prioritization of Goals | Ranking goals based on importance and feasibility | Ensures critical goals are funded first, optimizing resource use |
| Discipline in Saving and Investing | Encouraging consistent saving and strategic investment | Builds wealth steadily and avoids impulsive financial decisions |
| Risk Management | Protecting against unforeseen events with insurance and emergency funds | Prevents setbacks that could derail progress |
| Informed Decision-Making | Using data and financial analysis to guide choices | Minimizes mistakes and maximizes returns on investments |
| Progress Tracking and Motivation | Regularly reviewing financial status and milestones | Boosts confidence and allows timely adjustments |
| Adaptability to Life Changes | Updating plans based on changes in income, family, or market conditions | Keeps goals relevant and plans effective through all life stages |
| Tax and Expense Optimization | Implementing strategies to reduce tax burden and control expenses | Increases funds available to allocate toward goals |
| Promoting Long-Term Thinking | Encouraging delayed gratification and focus on future benefits | Strengthens commitment to goals and builds financial resilience |
Financial planning plays a pivotal role in turning your aspirations into achievable realities. Without a plan, goals remain mere wishes. Financial planning bridges the gap between where you are today and where you want to be tomorrow. It provides clarity, discipline, and structure, making the pursuit of your goals more systematic and less stressful.
Let’s break down how financial planning directly supports goal achievement in detail:
Provides Clear Direction Through Goal Setting
Financial planning begins with defining clear, specific, and measurable goals. Whether you want to buy a house, fund your child’s education, travel the world, or retire comfortably, financial planning forces you to articulate what success looks like.
- Why this matters: Clear goals transform vague desires into concrete targets, making it easier to formulate strategies, prioritize resources, and track progress.
- How it works: Financial planners use tools like SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to help you clarify exactly what you want and by when. This ensures your efforts and finances are aligned.
Creates a Realistic Roadmap with Actionable Steps
Once goals are set, financial planning lays out the roadmap, detailing how to get there step-by-step. This includes budgeting, saving, investing, and managing expenses.
- Why this matters: Without a roadmap, even the best intentions can fail due to lack of direction or unrealistic expectations.
- How it works: Your plan outlines how much money needs to be saved monthly, what investment returns are required, and what timelines are feasible. For example, if you want to buy a home in 5 years, the plan might specify saving a down payment of $50,000, investing in a mix of stocks and bonds, and adjusting your spending accordingly.
Prioritizes Financial Goals for Better Decision-Making
Life often presents multiple goals competing for your limited financial resources. Financial planning helps prioritize goals based on importance, urgency, and feasibility.
- Why this matters: Prioritization ensures that critical objectives are funded first, preventing dilution of resources and wasted effort.
- How it works: For instance, emergency savings and retirement might take precedence over discretionary spending like vacations or luxury goods. A planner will help you allocate resources effectively to ensure essential goals are secure before tackling secondary ones.
Encourages Discipline and Consistency in Saving and Investing
Financial planning embeds discipline into your financial habits by encouraging regular savings and thoughtful investments.
- Why this matters: Consistency is one of the most important factors in wealth accumulation and goal achievement. Sporadic saving or impulsive spending can undermine progress.
- How it works: Automated savings plans, monthly budget reviews, and investment schedules are common tools that instill discipline. For example, setting up automatic transfers to a retirement account ensures you save without needing to remember or resist temptation.
Helps Manage Risks to Avoid Financial Setbacks
Unexpected events — such as illness, job loss, or economic downturns — can threaten your financial goals. Financial planning includes risk management strategies to protect your progress.
- Why this matters: Without adequate protection, a single unexpected event can wipe out years of hard work.
- How it works: Insurance (health, life, disability), emergency funds, and diversified investments are all part of a solid financial plan. These safeguards act as buffers, helping you stay on track even when life throws curveballs.
Facilitates Informed Decision-Making with Data and Analysis
Financial planning relies on data — your income, expenses, assets, liabilities, market conditions, and tax laws — to make informed decisions.
- Why this matters: Emotional or uninformed decisions often lead to costly mistakes that delay or derail goals.
- How it works: For example, choosing the right investment vehicles based on risk tolerance and time horizon requires analysis. Financial planning tools and professional advice provide insights into how to maximize returns while minimizing risks, helping you make smarter choices.
Builds Confidence and Motivation by Tracking Progress
Financial planning includes regular monitoring and reviewing your progress, which builds confidence and motivation to stay committed.
- Why this matters: Seeing progress, even small wins, encourages continued effort and adherence to the plan.
- How it works: Monthly or quarterly reviews can highlight areas where you’re excelling and areas needing adjustment. This feedback loop helps you remain proactive rather than reactive, making course corrections as needed.
Adjusts for Life Changes to Keep Goals Relevant
Life is dynamic — your goals, income, family situation, or market conditions may change. Financial planning is not static; it adapts to changes, ensuring your goals remain realistic and achievable.
- Why this matters: Sticking rigidly to an outdated plan can be counterproductive or even harmful.
- How it works: Major events like marriage, childbirth, career changes, or economic shifts require revisiting your plan. Financial planning incorporates periodic reviews and revisions to keep your strategy aligned with your current reality.
Maximizes Resources by Efficient Tax and Expense Management
Financial planning optimizes your resources by employing tax-efficient strategies and controlling unnecessary expenses.
- Why this matters: Taxes and overspending can eat into your savings and slow goal achievement.
- How it works: Utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, claiming deductions, and budgeting effectively frees up more money for your goals. For example, contributing to a retirement plan can reduce taxable income while growing your savings.
Encourages Long-Term Thinking Beyond Immediate Gratification
Financial planning promotes delayed gratification by encouraging you to prioritize long-term benefits over short-term pleasures.
- Why this matters: Sacrificing immediate wants for future needs is challenging but essential for major goals like home ownership or retirement.
- How it works: By visualizing your goals and understanding the impact of your choices, financial planning builds the mindset necessary for sustained commitment and wise financial behavior.
Also Read: What Personal Finance Advice Should Everyone Know?
Conclusion
Financial planning is an essential tool for achieving your personal and family goals. It provides a structured approach to managing finances, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively to support aspirations. By setting clear objectives, creating a budget, saving and investing wisely, managing risks, optimizing taxes, planning for retirement, and preparing an estate plan, you can build a secure financial future.
FAQs
- What is financial planning?
Financial planning is the process of assessing your current financial situation, setting goals, and creating strategies to achieve them.
- Why is financial planning important?
It helps manage finances effectively, ensuring resources are allocated to meet personal and family goals.
- How do I start financial planning?
Begin by evaluating your income, expenses, debts, and assets. Then, set clear financial goals and develop a plan to achieve them.
- Can I do financial planning on my own?
Yes, many individuals can create their own financial plans. However, consulting with a financial advisor can provide expert guidance.
- How often should I review my financial plan?
It’s advisable to review your financial plan annually or whenever there are significant changes in your financial situation.
- What if my financial goals change?
Adjust your financial plan accordingly to reflect new goals, ensuring that your strategies remain aligned with your objectives.
- Is financial planning only for wealthy individuals?
No, financial planning is beneficial for individuals at all income levels, helping them manage their finances and achieve their goals.



